Ochota massacre

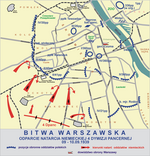
The Ochota Massacre (in Polish: Rzeź Ochoty – "Ochota slaughter") was a wave of German-orchestrated mass murder, looting, arson, torture and rape, which swept through the Warsaw district of Ochota from 4–25 August 1944, during the Warsaw Uprising. The principal perpetrators of these war crimes were the Nazi collaborationist S.S. Sturmbrigade R.O.N.A., the so-called "Russian National Liberation Army" (Russian: Русская Освободительная Народная Армия, RONA), commanded by Bronislav Kaminski. The worst atrocities were committed in the local hospitals, in the Curie Institute, the Kolonia Staszica housing estate, and the Zieleniak concentration camp. In all, about 10,000 residents of Ochota were killed and had their property stolen, after which the district was systematically burnt down by German forces, as were the bodies of many of the victims.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Ochota massacre (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Ochota massacre
Opaczewska, Warsaw Ochota (Warsaw)
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 52.21 ° | E 20.971 ° |
Address
Opaczewska 15
02-368 Warsaw, Ochota (Warsaw)
Masovian Voivodeship, Poland
Open on Google Maps