Sirkeci

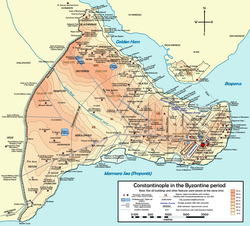
Sirkeci (pronounced [ˈsiɾkedʒi]) is a neighborhood in the Eminönü quarter of the Fatih district in Istanbul, Turkey. The neighborhood borders to the north the mouth of the Golden Horn, to the west the neighborhood of Bahçekapı, to the east the Topkapı Palace area, and to the south the Cağaloğlu neighborhood. It hosts the Sirkeci railway station, the easternmost terminus of the Orient Express, a historic long-distance passenger train service in Europe that operated between Paris and Istanbul in the period between 1883 and 2009.The neighborhood consists mostly of commercial and tourist-oriented buildings. A combination of small shops, hans (larger workshops) and offices intermingle with boutique hotels, traditional Turkish restaurants, Turkish and foreign-language bookstores, and tourist offices. In the Byzantine period, the area was known as Prosphorion (Ancient Greek: Προσφόριον).
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Sirkeci (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Sirkeci
Ankara Caddesi, Istanbul
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 41.014722222222 ° | E 28.975555555556 ° |
Address
Garanti Bankası
Ankara Caddesi
Istanbul
Türkiye
Open on Google Maps