Bryn Mawr, Minneapolis

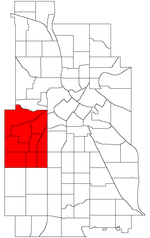
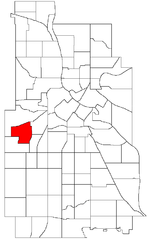
Bryn Mawr (pronounced from Welsh for "big hill") is a neighborhood within the Calhoun-Isles community in Minneapolis located directly west of downtown Minneapolis. Prior to the 1960s, the neighborhood was home to many workers of the nearby Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway yard. The neighborhood is all residential with two small business clusters, and a majority of it is surrounded by parks and hiking trails. The west-northwest border is adjacent to Theodore Wirth Park, while the southwestern perimeter borders Saint Louis Park.In addition to Theodore Wirth Park, Bryn Mawr is bound by more parkland: Bassett Creek to the north, the Bryn Mawr Meadows park to the east, and Cedar Lake and Cedar Lake park to the south. Nearby neighborhoods include Harrison to the north, Lowry Hill to the southeast, and Kenwood and Cedar-Isles-Dean to the south.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Bryn Mawr, Minneapolis (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Bryn Mawr, Minneapolis
Thomas Avenue South, Minneapolis Bde Maka Ska - Isles
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 44.9729 ° | E -93.3136 ° |
Address
Thomas Avenue South 420
55405 Minneapolis, Bde Maka Ska - Isles
Minnesota, United States
Open on Google Maps