City Pier A
Government buildings completed in 1886Government buildings on the National Register of Historic Places in ManhattanHistoric American Engineering Record in New York CityHudson RiverNew York City Designated Landmarks in Manhattan ... and 5 more
Piers in New York CityPiers on the National Register of Historic PlacesThe Battery (Manhattan)Transportation buildings and structures on the National Register of Historic Places in New York CityUse mdy dates from August 2019
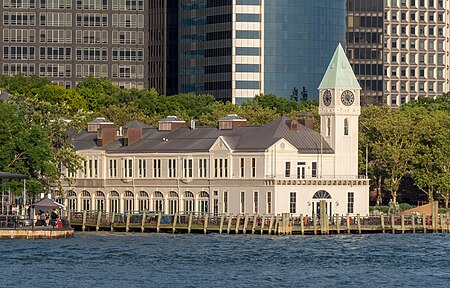
Pier A Harbor House (commonly referred to as City Pier A) is a municipal pier in the Hudson River at Battery Park in Lower Manhattan, New York City. It is sometimes nicknamed the "Liberty Gateway" despite never having been a major disembarkation point. Pier A is the last surviving historic pier in the city.The Pier was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1975, and was designated a New York City landmark in 1977.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article City Pier A (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).City Pier A
Battery Place, New York Manhattan
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address External links Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 40.704166666667 ° | E -74.018333333333 ° |
Address
City Pier A
Battery Place 22
10004 New York, Manhattan
New York, United States
Open on Google Maps







