Addiscombe East (ward)
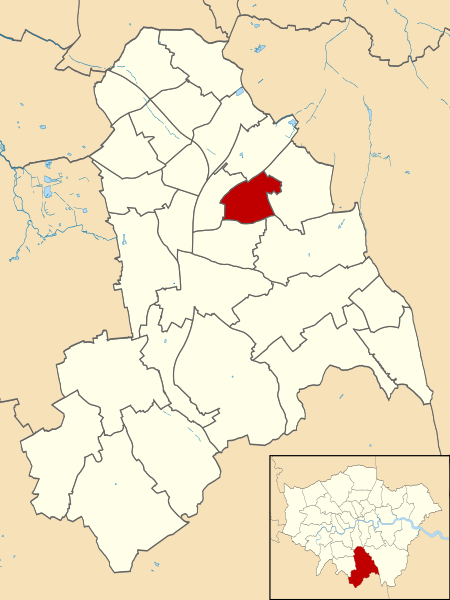
Addiscombe East is a ward in the London Borough of Croydon, in London in the United Kingdom. The ward replaced the former Ashburton Ward, which covered the Ashburton area, as well as covering the main retail area of Addiscombe, the Stroud Green, Tollgate and Longheath Garden estates, and large parts of northern Shirley. The population of the former ward at the 2011 Census was 14,721.The ward currently forms part of the Croydon Central constituency, which is one of the most marginal in the country. In 2015, only 165 votes separated the Conservatives and Labour. The ward returns two councillors every four years to Croydon Council. At the 2018 London local elections Maddie Henson and Jeet Bains were elected. They were both re-elected at the 2022 London local elections.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Addiscombe East (ward) (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Addiscombe East (ward)
Coleridge Road, London Wood Side (London Borough of Croydon)
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 51.385 ° | E -0.057 ° |
Address
Coleridge Road
Coleridge Road
CR0 7BT London, Wood Side (London Borough of Croydon)
England, United Kingdom
Open on Google Maps








