International House of New York
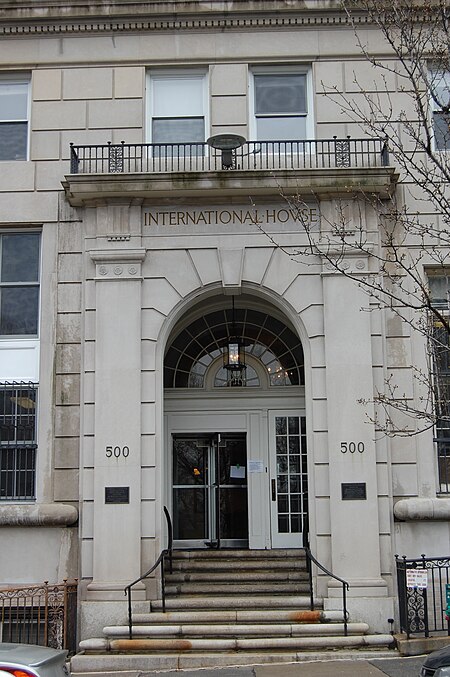

International House New York, also known as I-House, is a private, independent, non-profit residence and program center for postgraduate students, research scholars, trainees, and interns, located at 500 Riverside Drive in Morningside Heights, Manhattan, New York City. The I-House residential community typically consists of 700+ students and scholars from over 100 countries annually, with about one-third of those coming from the United States. The residential experience includes programming designed to promote mutual respect, friendship, and leadership skills across cultures and fields of study. International House has attracted prominent guest speakers through the years, from Eleanor Roosevelt and Isaac Stern to Sandra Day O'Connor, Valerie Jarrett, George Takei, and Nelson Mandela. Students attend various universities and schools throughout the city, which include Columbia University, Juilliard School, Actors' Studio Drama School, New York University, the Manhattan School of Music, the Union Theological Seminary in the City of New York, Teachers College, Columbia University, and the City University of New York.The original entrance to International House is inscribed with the motto written by John D. Rockefeller Jr.: "That Brotherhood May Prevail"; the piazza (The Abby O'Neill Patio) of its entrance opens onto Sakura Park, the site of Japan's original gift of cherry trees to New York City in 1912. The 500 Riverside Drive building, designed in the Italianite style by architects Louis E. Jallade and Marc Eidlitz and Sons, was built in 1924 and was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places as International House in 1999.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article International House of New York (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).International House of New York
Riverside Drive, New York Manhattan
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 40.813611111111 ° | E -73.961944444444 ° |
Address
Riverside Drive
Riverside Drive
10115 New York, Manhattan
New York, United States
Open on Google Maps