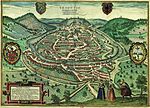
Battant (Besançon)

Battant is one of the oldest parts of Besançon, Doubs, France, and has been under architectural protection since 1964. It is situated on the right bank of the river Doubs, north of the ox-bow that encircles the center of the city. A bridge across the Doubs joins the two quarters Battant and La Boucle (The Oxbow), via the Vauban quay and Jouffroy d'Abbans Place. Today, Battant has become a popular district with a diverse population, numbering about 4,200 people. It is one of the more lively quarters of the city because of its numerous small shops, its nightlife, and its market. The quarter's name appears to have come from the Mouillère, a small brook also known as the fons batenti (river of the beater) because the water from the brook drove a cloth-beating device. The name came to be applied to a nearby street, and then by extension to the entire quarter. The inhabitants of Battant are known as Bousbots, which recalls the resistance that the grape growers of the district gave to the attempted seizure of the city by the Huguenots of Montbéliard on the night of 20–21 June 1575.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Battant (Besançon) (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Battant (Besançon)
Rue de la Madeleine, Besançon Rue Battant
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 47.240555555556 ° | E 6.0194444444444 ° |
Address
Intervista RH
Rue de la Madeleine
25000 Besançon, Rue Battant
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, France
Open on Google Maps