Jufuku-ji
1200 establishments in Asia1200s establishments in Japan13th-century Buddhist templesBuddhist temples in Kamakura, KanagawaInfobox religious building with unknown affiliation ... and 2 more
Kenchō-ji templesRinzai temples

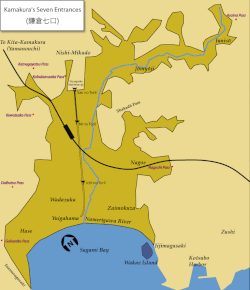
Kikokuzan Kongō Jufuku Zenji (亀谷山金剛寿福禅寺), usually known as Jufuku-ji, is a temple of the Kenchō-ji branch of the Rinzai sect and the oldest Zen temple in Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. Ranked third among Kamakura's prestigious Five Mountains, it is number 24 among the Thirty-Three Kamakura Kannon (鎌倉三十三観音, Kamakura Sanjūsan Kannon) pilgrimage temples and number 18 of the Kamakura Nijūyon Jizō (鎌倉二十四地蔵) temples. Its main object of worship is Shaka Nyorai.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Jufuku-ji (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Jufuku-ji
Kamakura
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 35.32417 ° | E 139.54903 ° |
Address
248-0005 Kamakura
Japan
Open on Google Maps