Siege of Havana

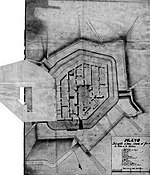
The siege of Havana was a successful British siege against Spanish-ruled Havana that lasted from March to August 1762, as part of the Seven Years' War. After Spain abandoned its former policy of neutrality by signing the family compact with France, resulting in a British declaration of war on Spain in January 1762, the British government decided to mount an attack on the important Spanish fortress and naval base of Havana, with the intention of weakening the Spanish presence in the Caribbean and improving the security of its own North American colonies. A strong British naval force consisting of squadrons from Britain and the West Indies, and the military force of British and American troops it convoyed, were able to approach Havana from a direction that neither the Spanish governor nor the Admiral expected and were able to trap the Spanish fleet in the Havana harbour and land its troops with relatively little resistance. The Spanish authorities decided on a strategy of delaying the British attack until the strength of the city's defences and the onset of seasonal rains inflicting tropical diseases would significantly reduce the size of the British force via disease, along with the start of hurricane season would force the British fleet to seek a safe anchorage. However, the city's main fortress, the Morro Castle was overlooked by a hill that the governor had neglected to fortify; the British installed batteries there and bombarded the fortress daily with heavy shelling. The fortress eventually fell after the officer in charge of Morro Castle, Luis Vicente de Velasco, was mortally wounded by a stray bullet. The capture of Morro Castle led to the eventual fall of the rest of the fortifications and the surrender of the city, the remaining garrison, and the naval forces present, before the hurricane season began. The surrender of Havana led to substantial rewards for the British naval and military leaders and smaller amounts of prize money for other officers and men. The Spanish governor, Admiral and other military and civil office holders were court-martialled upon their return to Spain and punished for their failures to conduct a better defence and allowing the Spanish fleet present to fall intact into the hands of the British. Havana remained under British occupation until February 1763, when it was returned to Spain under the 1763 Treaty of Paris that formally ended the war.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Siege of Havana (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Siege of Havana
Milagros,
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 23.0964 ° | E -82.3747 ° |
Address
Milagros
Milagros
10700 (Santos Suárez)
Havana, Cuba
Open on Google Maps