Ajuria Enea

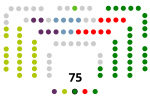
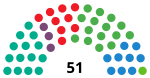
The Palace of Ajuria Enea (Basque for "My Ajuria") is a building in Vitoria-Gasteiz, northern Spain. It is the official residence of the Lehendakari (the President of the Basque Autonomous Community). The building, chosen to be official residence on the basis of its architectural merits, was purchased by the Basque Government from its former owner, the Provincial Council of Álava, in 1980. That same year it was occupied by Carlos Garaikoetxea, first President of the Basque Government after the restoration of democracy in Spain. The palace, which was built in 1920 by Swiss architect Alfredo Baeschlin and contractor Hilarión San Vicente for local industrialist Serafín Ajuria, displays architectural elements of neo-Basque art on the façade. After being the residence of the Ajuria family, in 1966 it was handed over to the religious order of the Madres Escolapias, who used it as a school. Six years later, in 1972, it was purchased by the Provincial Council of Álava for conversion into a museum of Basque art, and it was open to the public for two years until it became the Lehendakari's official residence.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Ajuria Enea (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Ajuria Enea
Frai Francisco Vitoria ibilbidea/Paseo Fray Francisco de Vitoria, Vitoria-Gasteiz Mendizorrotza
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address External links Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 42.8408 ° | E -2.67889 ° |
Address
Ajuria Enea
Frai Francisco Vitoria ibilbidea/Paseo Fray Francisco de Vitoria 5
01007 Vitoria-Gasteiz, Mendizorrotza
Autonomous Community of the Basque Country, Spain
Open on Google Maps