Southeast (Washington, D.C.)
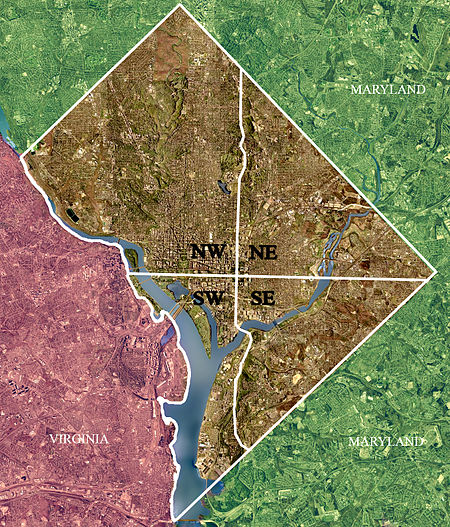
Southeast (SE or S.E.) is the southeastern quadrant of Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States, and is located south of East Capitol Street and east of South Capitol Street. It includes the Capitol Hill and Anacostia neighborhoods, the Navy Yard, the Joint Base Anacostia-Bolling (JBAB), the U.S. Marine Barracks, the Anacostia River waterfront, Eastern Market, the remains of several Civil War-era forts, historic St. Elizabeths Hospital, RFK Stadium, Nationals Park, and the Congressional Cemetery. It also contains a landmark known as "The Big Chair," located on Martin Luther King Jr. Avenue. The quadrant is split by the Anacostia River, with the portion that is west of the river sometimes referred to as "Near Southeast". Geographically, it is the second-smallest quadrant of the city.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Southeast (Washington, D.C.) (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Southeast (Washington, D.C.)
17th Place Southeast, Washington
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 38.87 ° | E -76.98 ° |
Address
17th Place Southeast 1625
20020 Washington
District of Columbia, United States
Open on Google Maps







