Zinc-lead deposits in Wiesloch
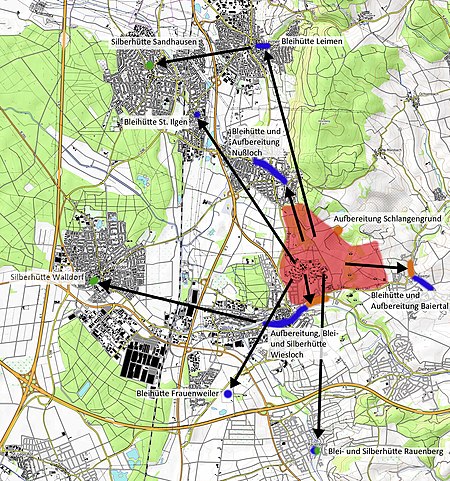
The area around Wiesloch, Germany, is a historical centre for mining, running between Roman times and the earlier 2000s. The area is situated on the eastern edge of the Upper Rhine Plain and contains large concentrations of carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits. Lime (Kalk) for cement is still actively mined in the vicinity, with most of the clay pits closed, and the last heavy metal mine operated until 1953 by Stolberger Zink. On top of the escarpment metals and lime have been mined, with clay and sand mined at the end of the valley floor where faulting has brought different layers closer to the surface. During the 11th century, around ~100 tonnes of silver is estimated to have been mined, contributing financially to the area and liking funding the creation of Speyer Cathedral.Along the length of the River Leimbach are spoil tips from historic mining.The Nussloch quarry extracting lime for cement and belonging to HeidelbergCement was anticipated to reach permitted limits for extraction during the late-2020s.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Zinc-lead deposits in Wiesloch (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Zinc-lead deposits in Wiesloch
Wieslocher Straße, Verwaltungsgemeinschaft Wiesloch
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 49.3 ° | E 8.72 ° |
Address
Wieslocher Straße
Wieslocher Straße
69168 Verwaltungsgemeinschaft Wiesloch (Baiertal)
Baden-Württemberg, Germany
Open on Google Maps