The Headlands

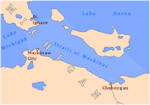
The Headlands International Dark Sky Park is a 550-acre (220 ha) county park in the U.S. state of Michigan. The park preserves over 2 mi (3.2 km) of undeveloped Lake Michigan shoreline south and west of McGulpin Point Light in the Straits of Mackinac. It is located in, and is operated by, Emmet County in Northern Michigan. The nearest town is Mackinaw City, Michigan. The park contains woodlands and many species of rare and endangered plant life. Park fauna include the black bear, whitetail deer, coyotes, bald eagles, osprey, and the wild turkey. Marked trails are provided for hiking, photography, bicycling and cross-country skiing. In May 2011, Headlands Park was awarded International Dark Sky Park designation by the International Dark-Sky Association. It was the 6th such park in the United States, and the 9th such park worldwide, to be awarded this designation. Park signage celebrates astronomy and the heritage of the Native Americans of Northern Michigan.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article The Headlands (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).The Headlands
Ridgeline Trail, Wawatam Township
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 45.783333333333 ° | E -84.783333333333 ° |
Address
Ridgeline Trail
Ridgeline Trail
Wawatam Township
Michigan, United States
Open on Google Maps