McGulpin Point Light
1869 establishments in MichiganHouses completed in 1869Lighthouse museums in MichiganLighthouses completed in 1869Lighthouses in Michigan ... and 1 more
Museums in Emmet County, Michigan

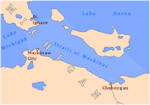
McGulpin Point Light was constructed as a navigational aid through the Straits of Mackinac. The light began operation in 1869, making it one of the oldest surviving lighthouses in the Straits. Only in operation until 1906, the light is located on McGulpin Point, (500 Headlands Road), approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) west of Fort Michilimackinac. McGulpin Point Lighthouse & Historic Site has been owned by Emmet County since 2008 and the facility has been an official private Aid to Navigation on the NOAA chart map since 2009. Tours were available during the 2019 season for a small fee.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article McGulpin Point Light (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).McGulpin Point Light
Headlands Road, Wawatam Township
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address External links Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 45.7869 ° | E -84.7722 ° |
Address
McGulpin Point Lighthouse
Headlands Road
49701 Wawatam Township
Michigan, United States
Open on Google Maps