Compact Muon Solenoid
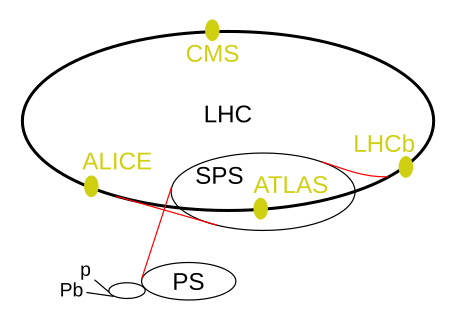
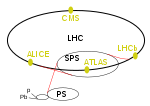
The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment is one of two large general-purpose particle physics detectors built on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland and France. The goal of the CMS experiment is to investigate a wide range of physics, including the search for the Higgs boson, extra dimensions, and particles that could make up dark matter. CMS is 21 metres long, 15 m in diameter, and weighs about 14,000 tonnes. Over 4,000 people, representing 206 scientific institutes and 47 countries, form the CMS collaboration who built and now operate the detector. It is located in a cavern at Cessy in France, just across the border from Geneva. In July 2012, along with ATLAS, CMS tentatively discovered the Higgs boson. By March 2013 its existence was confirmed.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Compact Muon Solenoid (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Compact Muon Solenoid
A9,
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 46.309444444444 ° | E 6.0769444444444 ° |
Address
A9
1823
Vaud, Suisse
Open on Google Maps