St. Volodymyr's Ukrainian Orthodox Cathedral (Toronto)
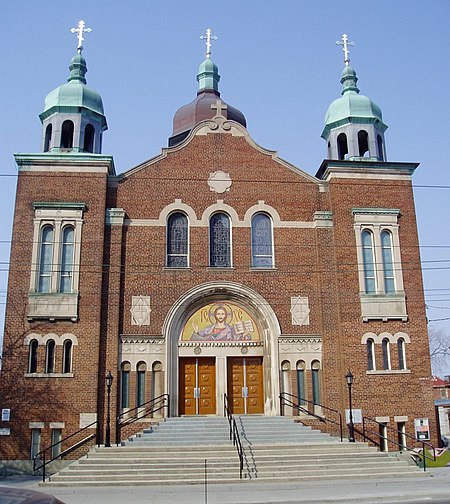

St. Volodymyr's Ukrainian Orthodox Cathedral is a Ukrainian Orthodox Cathedral in Toronto, Ontario, Canada located on Bathurst Street just to the west of Kensington Market. The majority of the first Ukrainian immigrants to Canada were Eastern Catholic believers with only a small fraction belonging to the Eastern Orthodox faith. This changed with later waves of immigration that saw more people coming from the Orthodox east. The first Ukrainian Orthodox Union in Toronto was established in 1926. For several years they met in rented halls and in churches of other denominations. The land on Bathurst was purchased in 1935. Work on the cathedral began in 1946 and was completed two years later. The cathedral is in the standard Byzantine style used throughout Ukraine.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article St. Volodymyr's Ukrainian Orthodox Cathedral (Toronto) (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).St. Volodymyr's Ukrainian Orthodox Cathedral (Toronto)
Bathurst Street, Toronto
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Phone number Website External links Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 43.653845 ° | E -79.406932 ° |
Address
St. Volodymir Ukrainian Orthodox Cathedral
Bathurst Street 400
M5T 2S6 Toronto
Ontario, Canada
Open on Google Maps