St Benet Gracechurch
1868 disestablishments in EnglandBuildings and structures demolished in 1868Christopher Wren church buildings in LondonChurches rebuilt after the Great Fire of London but since demolished
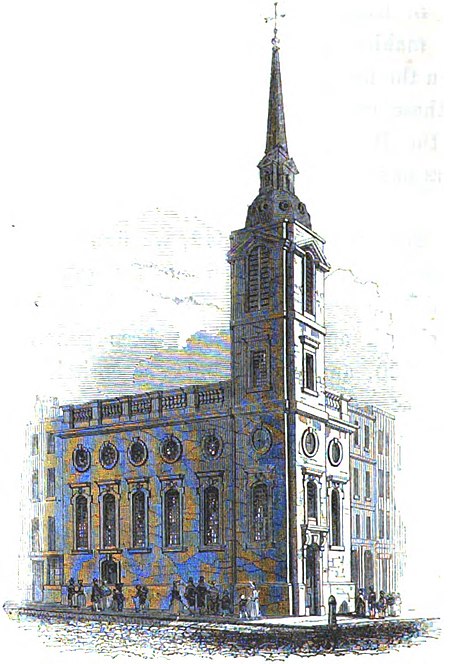
St Benet Gracechurch (or Grass Church), so called because a haymarket existed nearby (Cobb), was a parish church in the City of London. First recorded in the 11th century, it was destroyed in the Great Fire of London of 1666 and rebuilt by the office of Sir Christopher Wren. The church was demolished in 1868.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article St Benet Gracechurch (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).St Benet Gracechurch
Gracechurch Street, City of London
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 51.511666666667 ° | E -0.085 ° |
Address
Allianz
Gracechurch Street 60
EC3V 0EE City of London
England, United Kingdom
Open on Google Maps











