Angkor (Khmer: អង្គរ [ʔɑŋkɔː], lit. 'Capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura (Khmer: យសោធរបុរៈ; Sanskrit: यशोधरपुर), was the capital city of the Khmer Empire. The city and empire flourished from approximately the 9th to the 15th centuries. The city houses the Angkor Wat, one of Cambodia's most popular tourist attractions.
The name Angkor is derived from nokor (នគរ), a Khmer word meaning "kingdom" which in turn derived from Sanskrit nagara (नगर), meaning "city". The Angkorian period began in AD 802, when the Khmer Hindu monarch Jayavarman II declared himself a "universal monarch" and "god-king", and lasted until the late 14th century, first falling under Ayutthayan suzerainty in 1351. A Khmer rebellion against Siamese authority resulted in the 1431 sacking of Angkor by Ayutthaya, causing its population to migrate south to Longvek. The alternate name, Yasodharapura, was derived from the name of the foster mother of Lord Krishna in Hinduism. Hinduism was the largest religion in the ancient Khmer Empire, and many temples were constructed by Khmer kings dedicated to Hindu deities, including Angkor Wat.
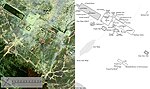
The ruins of Angkor are located amid forests and farmland north of the Great Lake (Tonlé Sap) and south of the Kulen Hills, near modern-day Siem Reap city (13°24′N, 103°51′E), in Siem Reap Province. The temples of the Angkor area number over one thousand, ranging in scale from nondescript piles of brick rubble scattered through rice fields to the Angkor Wat, said to be the world's largest single religious monument. Many of the temples at Angkor have been restored, and together, they comprise the most significant site of Khmer architecture. Visitors approach two million annually, and the entire expanse, including Angkor Wat and Angkor Thom is collectively protected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The popularity of the site among tourists presents multiple challenges to the preservation of the ruins.
In 2007, an international team of researchers using satellite photographs and other modern techniques concluded that Angkor had been the largest pre-industrial city in the world by surface area, with an elaborate infrastructure system connecting an urban sprawl of at least 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi) to the well-known temples at its core. Angkor is considered to be a "hydraulic city" because it had a complicated water management network, which was used for systematically stabilizing, storing, and dispersing water throughout the area. This network is believed to have been used for irrigation in order to offset the unpredictable monsoon season and to also support the increasing population. Although the size of its population remains a topic of research and debate, newly identified agricultural systems in the Angkor area may have supported between 750,000 and one million people.