Ebsdorfergrund
Marburg-BiedenkopfMunicipalities in Hesse

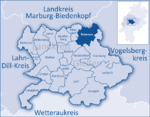
Ebsdorfergrund is a municipality consisting of eleven villages in the southeast of Marburg-Biedenkopf district in Hesse, Germany. The community's municipal area extends over the Ebsdorfer Grund in the valley of the Zwester Ohm and the areas around its edges, connecting the Amöneburg Basin with the middle Lahn valley between Marburg and Gießen. Through the municipal area runs a highway from Fronhausen (Autobahn interchange in Gießen by Bundesstraße B 3) to Kirchhain. Another one joins Marburg with Grünberg. The old ring railway, the Marburger Kreisbahn, which opened in 1905 and ran through the municipal area to Dreihausen, was shut down in 1972.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Ebsdorfergrund (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Ebsdorfergrund
Sembergsweg, Ebsdorfergrund
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 50.733333333333 ° | E 8.8666666666667 ° |
Address
Sembergsweg
35085 Ebsdorfergrund
Hesse, Germany
Open on Google Maps