Saint Alban's Abbey, Mainz
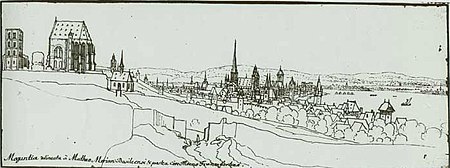
St. Alban's Abbey, Mainz (Stift St. Alban vor Mainz) originated as a Benedictine abbey, founded in 787 or 796 by Archbishop Richulf (787–813) in honour of Saint Alban of Mainz, located to the south of Mainz on the hill later called the Albansberg. It was turned into a collegiate foundation (Herrenstift) in 1442. The buildings were entirely destroyed in 1552, although the foundation retained a legal existence until its formal dissolution in 1802. The abbey was initially renowned for its school, and for its beautiful church. The school was the origin of the Carolingian court school. One of its famous teachers was Rabanus Maurus, born c 780 in Mainz. The importance of the place was reflected in the extraordinary size of the hall. The church was inaugurated on 1 December 805 by Richulf and remained the largest church of Mainz until construction of Mainz Cathedral was begun by Willigis.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Saint Alban's Abbey, Mainz (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Saint Alban's Abbey, Mainz
Am Rosengarten, Mainz Oberstadt (Oberstadt)
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 49.99 ° | E 8.28 ° |
Address
Am Rosengarten 29
55131 Mainz, Oberstadt (Oberstadt)
Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
Open on Google Maps









