Victoria Dock (Melbourne)

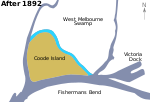
Victoria Dock is a large excavated harbour basin located off Footscray Road and Docklands Highway, Docklands, in Melbourne. It was constructed between 1887 and 1892, under the supervision of Melbourne Harbor Trust engineer Joseph Brady, to modified designs of British engineer Sir John Coode. It is the oldest and largest surviving single dock in the world. The water basin covers 37.6 hectares (96 acres) and the entrance at the western end is 61 metres wide. It was built to accommodate ships of 9.5m draft, with initially timber wharf sheds and wharfs around the perimeter, supplemented by a piled timber central pier in 1919 extending from the east edge of the dock. At its greatest extent it accommodated 21 berths, although this has been substantially reduced as the land area has been redeveloped for the Docklands commercial and residential towers. The Central Pier, a later addition, retains two sheds but has been reduced to half its size. It was used as a dance venue, events, functions and entertainment until August 2019 when it was declared unsafe. In January 2020 it was shut down indefinitely because it would take "tens of millions of dollars" to rebuild to a safe standard.Portal and semi portal level luffing cranes once served timber and steel framed wharf sheds, all but three of which have been demolished. The oldest, dating from 1913, were along the eastern edge and were purported to have been dismantled for future restoration of the central pier sheds, two of which survive. All the cranes have been removed but crane rails survive on some wharf aprons. In the 1950s the dock handled over two million tons of cargo annually, increasing to 20 million revenue tons annually by the mid-1980s. However, increases in container shipping and the move of the one roll-on roll-off berth led to its abandonment for commercial shipping, and subsequent reuse of the area for development. The dock is included on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR H1720) and National Trust Register and is considered to be of Local, State, National and International significance.Coode Canal and Victoria Dock received an Engineering Heritage Marker from Engineers Australia as part of its Engineering Heritage Recognition Program.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Victoria Dock (Melbourne) (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Victoria Dock (Melbourne)
Coode Road, Melbourne West Melbourne
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N -37.81 ° | E 144.92 ° |
Address
Coode Road
3008 Melbourne, West Melbourne
Victoria, Australia
Open on Google Maps