Hispania
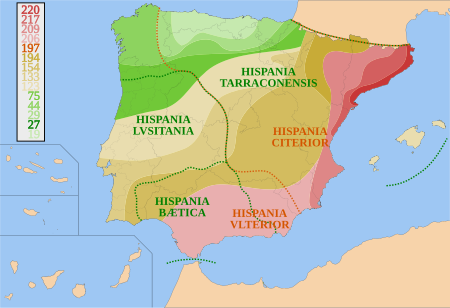
Hispania (Ancient Greek: Ἱσπανία, romanized: Hispanía; Latin: Hispānia [hɪsˈpaːnia]) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western part of Tarraconensis was split off, initially as Hispania Nova, which was later renamed "Callaecia" (or Gallaecia, whence modern Galicia). From Diocletian's Tetrarchy (AD 293) onwards, the south of the remainder of Tarraconensis was again split off as Carthaginensis, and all of the mainland Hispanic provinces, along with the Balearic Islands and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana, were later grouped into a civil diocese headed by a vicarius. The name Hispania was also used in the period of Visigothic rule. The modern place names of Spain and Hispaniola are both derived from Hispania.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Hispania (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Hispania
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 40.21 ° | E -4.35 ° |
Address
Cordón de la Fuente
45900
Castile-La Mancha, Spain
Open on Google Maps











