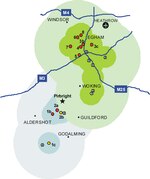
The 2007 United Kingdom foot-and-mouth outbreak occurred when the discharge of infectious effluent from a laboratory in Surrey led to foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) infections at four nearby farms. The infections were detected via regular livestock testing by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra).
The first diagnosis took place in a field of Normandy, Surrey; the second was three days later in a cattle-rotation field of a farm in Elstead, and the following day a third infection was found nearby within a quickly-established protection zone around the first detection. One month and ten days after the first diagnosis a final incidence of 2007 was identified and dealt with 13 miles (21 km) north of the first diseased animal. The source of the strain released and contained in Surrey in 2007 was the advanced effluent pipes from either the Institute for Animal Health or the similar vaccine researching and producing Merial Animal Health laboratory near to Pirbright village in the county. An inspection of the effluent pipes and manholes carried out by Health and Safety Executive investigators showed deficiencies, and the independent investigation of Brian Spratt concluded that it was very likely that they occasionally leaked still-infectious effluent at the time of the outbreak. Both laboratories, either of which may have been the cause, upgraded and repaired their effluent treatment systems to continue operation. The UK government provided compensation for the farmers directly involved.
These interrelated and contained events prompted precautionary measures of restricted-access containment zones in three counties where suspected infections were reported and major international trading partners such as Canada and the Republic of Ireland placed temporary restrictions on meat and dairy exports.