Andijk

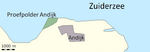
Andijk (Dutch: [ɑnˈdɛik] ; West Frisian: Andìk) is a former municipality and a village bordering Lake IJssel in the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland and the region of West-Frisia. Since 1 January 2011 Andijk has been part of Medemblik municipality. The name Andijk comes from the Dutch: aan de dijk, lit. 'at the dike'. In 1667, a small church was built. During the French Napoleonic occupation, Andijk became an independent municipality on 1 January 1812 by imperial decree of 21 October 1811. Andijk has fertile clay soil used for with agriculture and vegetable horticulture. Andijk is also an important supplier of drinking water for the region. A 40-hectare (99-acre) test polder, which was built in the Zuiderzee in 1926–1927 as a test run for the construction of the Wieringermeer polder, is located at Andijk. The polder is used for recreation, and has facilities for overnight stays, such as several camp-sites, two hunting points, and a beach.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Andijk (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Andijk
Beldersweg, Medemblik
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 52.75 ° | E 5.22 ° |
Address
Beldersweg 23
1619 GC Medemblik
North Holland, Netherlands
Open on Google Maps