Saginaw City, Michigan
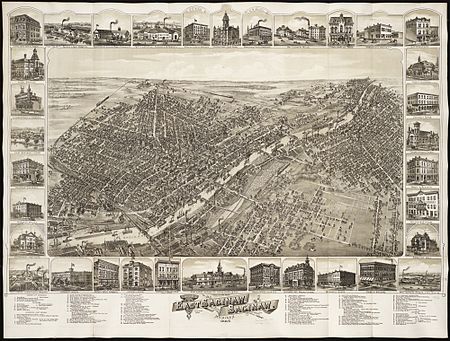
For the current city, see Saginaw, Michigan The City of Saginaw (Saginaw City) is a defunct city in Saginaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan that has been consolidated into a new municipality bearing the same name. To distinguish between the currently existing City of Saginaw and the former City of Saginaw, the name Saginaw City is used for the defunct city even though it was never incorporated under that name or called such during its time. The first permanent white settlement in the area was a fur-trading post on the west side of the Saginaw River established in 1816 by Louis Campau. The U.S. federal government extinguished Native American interests for most of the land in the area with the Treaty of Saginaw in 1819, clearing the way for white settlers. In 1822 the post became Fort Saginaw. Campau platted the town in 1823.Saginaw City was incorporated as a city in 1857. On June 2, 1889, the Michigan State Legislature passed an act to consolidate the cities of Saginaw City and East Saginaw to form the present-day city of Saginaw, which became effective with the election of officers for the consolidated city in March 1890.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Saginaw City, Michigan (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Saginaw City, Michigan
Court Street, Saginaw
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 43.417777777778 ° | E -83.964444444444 ° |
Address
Court Street 506
48602 Saginaw
Michigan, United States
Open on Google Maps









