Stapelholm
Former Ämter in Schleswig-HolsteinSchleswig-Flensburg geography stubs
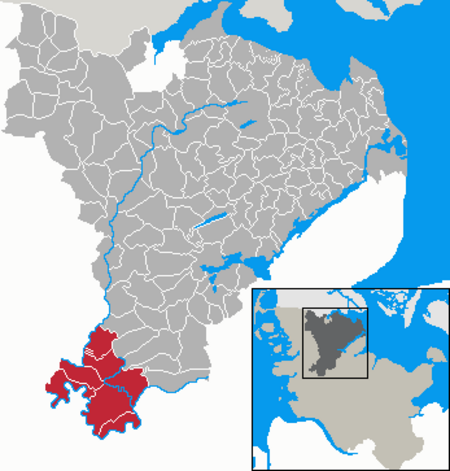
Stapelholm was an Amt ("collective municipality") in the district of Schleswig-Flensburg, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It was situated on the north bank of the river Eider, approx. 25 km southwest of Schleswig. The seat of the Amt was in Norderstapel. In January 2008, it was merged with the Amt Kropp to form the Amt Kropp-Stapelholm.The Amt Stapelholm consisted of the following municipalities: Bergenhusen Erfde Meggerdorf Norderstapel Süderstapel Tielen Wohlde
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Stapelholm (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Stapelholm
Alter Bahndamm, Kropp-Stapelholm
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 54.35 ° | E 9.25 ° |
Address
Alter Bahndamm
Alter Bahndamm
25879 Kropp-Stapelholm, Süderstapel
Schleswig-Holstein, Germany
Open on Google Maps







