Second Battle of Ream's Station
1864 in VirginiaAugust 1864 eventsBattles of the American Civil War in VirginiaBattles of the Eastern Theater of the American Civil WarConfederate victories of the American Civil War ... and 3 more
Conflicts in 1864Dinwiddie County in the American Civil WarPetersburg Campaign

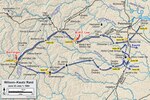
The Second Battle of Ream's Station (also Reams or Reams's) was fought during the siege of Petersburg in the American Civil War on August 25, 1864, in Dinwiddie County, Virginia. A Union force under Maj. Gen. Winfield S. Hancock began destroying part of the Petersburg Railroad, which was a vital supply line for Gen. Robert E. Lee's Confederate army in Petersburg, Virginia. Lee sent a force under Lt. Gen. A. P. Hill to challenge Hancock and the Confederates were able to rout the Union troops from their fortifications at Reams Station. However, they lost a key portion of the railroad, causing further logistical difficulties for the remainder of the Richmond-Petersburg Campaign.
Excerpt from the Wikipedia article Second Battle of Ream's Station (License: CC BY-SA 3.0, Authors, Images).Second Battle of Ream's Station
Halifax Road,
Geographical coordinates (GPS) Address Nearby Places Show on map
Geographical coordinates (GPS)
| Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|
| N 37.0959 ° | E -77.4226 ° |
Address
Halifax Road
Halifax Road
23830
Virginia, United States
Open on Google Maps